Model of accumulation, preservation and dissemination of research output and activities (2018)
Authors: Lina Bloveščiūnienė and Vilius Kučiukas.
Project objective
Project objective – create a model of accumulation, preservation and dissemination of Vytautas Magnus University (VDU) research output and research information, that enables:
- To improve the visibility of research output, activities and researchers in the world.
- To accumulate and ensure the long-term preservation of VDU research output and performance results.
- To increase the availability and accessibility of research output through open access.
- To optimize the administration of research activities.
Visibility of research output, activities and scientists in the world
Objects:
- Research publications.
- Researchers profiles, CV.
- Research projects.
- University structural departments, clusters.
Means:
- VDU website.
- Repository DSpace / CRIS.
- ORCID.
- Research output dissemination system.
Should influence:
- Increase rankings.
- Increase visibility and citations.
Accumulate and ensure long-term preservation of VDU research output and research performance results. Availability of research output through open access
Objects:
- Full-text documents of research publications.
- Full-text documents of master theses and doctoral dissertations (and summaries).
- Research journals.
Means:
- Repository DSpace / CRIS.
- Permanent URL's, long-term preservation.
- Research output dissemination system.
Should influence:
- Improving quality of studies.
- Increasing quality of research.
- Accumulating VDU research output and ensuring long-term preservation.
Optimization of administration of scholarly activity
Objects:
- Reports for the Ministry of Education, Science and Sport (ŠMSM), Research Council of Lithuania (LMT), MOSTA.
- Certifications.
- Qualifying contests.
- Statistics.
Should influence:
- Increased VDU rankings in assessment.
- Managing practical tools for research work, also for preparing reports.
- Improving scholars’ qualification.
Model of research output and dissemination of activities on the internet
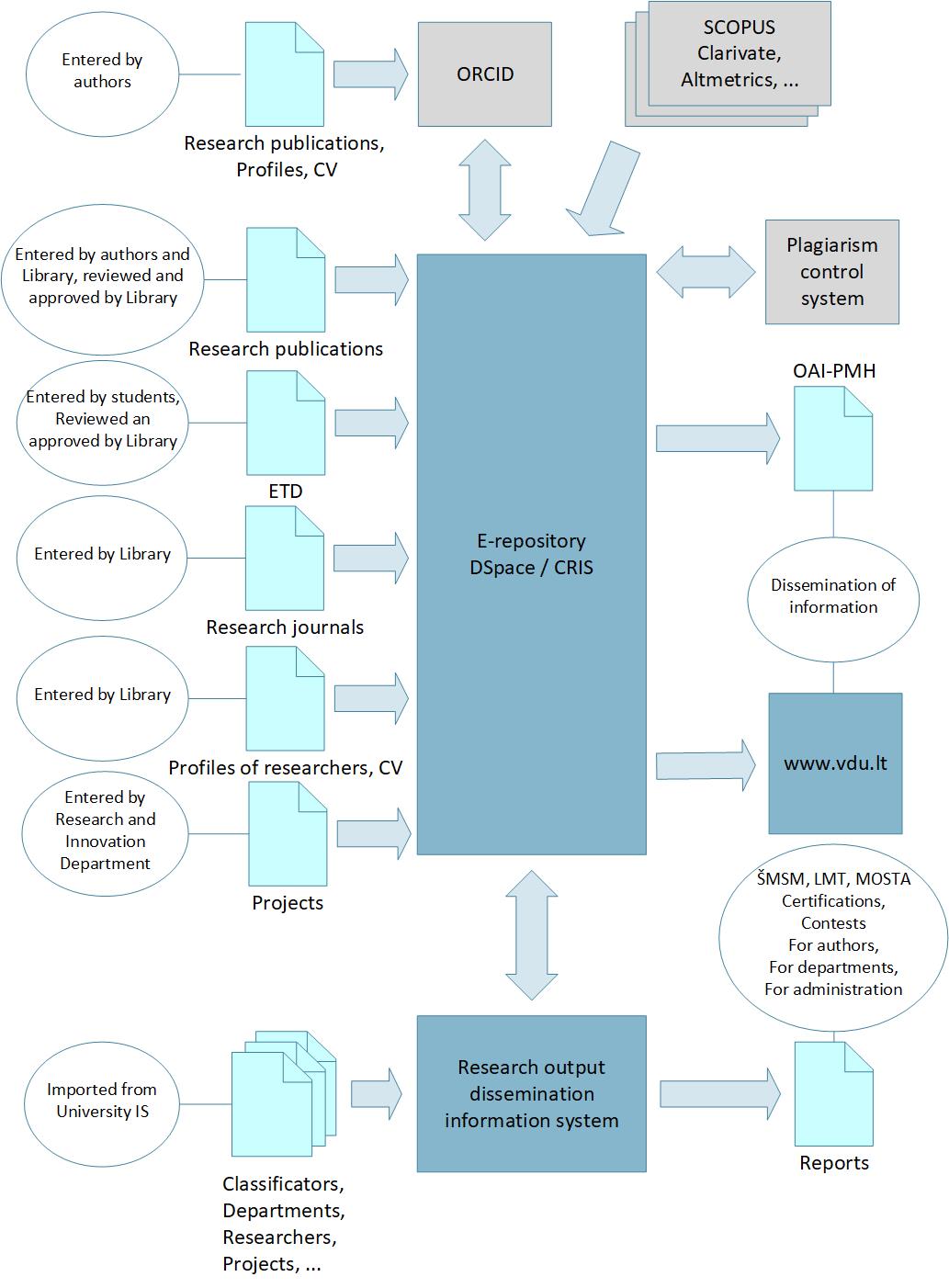
E-repository (DSpace / CRIS)
DSpace is an open source repository software package typically used for creating open access repositories for scholarly and/or published digital content (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DSpace). While DSpace shares some feature overlap with content management systems and document management systems, the DSpace repository software serves a specific need as a digital archives system, focused on the long-term storage, access and preservation of digital content.
DSpace / CRIS is the first free open-source extension of DSpace for the Research Data and Information Management ever developed (https://wiki.duraspace.org/display/DSPACECRIS/DSpace-CRIS+Home). Differently from other (commercial) CRISs (star), DSpace-CRIS has the institutional repository has its core component, providing high visibility on the web to all the collected information and objects. DSpace / CRIS is compliant with CERIF standard (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EuroCRIS).
A current research information system (CRIS) is a database or other information system to store, manage and exchange contextual metadata for the research activity funded by a research funder or conducted at a research-performing organisation (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Current_research_information_system).
DSpace accumulates research publications of scholars, final theses and dissertations (ETD), research journals. Together with descriptive Dublin Core (DC) standard publications may include full-text documents (e.g. in PDF format). Publications can be assigned to one or more thematic collections
CRIS collects information about scientists, projects and departments. Publications in DSpace are linked to scientists, departments and projects in CRIS.
DSpace / CRIS provides cross-links between publications and authors, departments and projects. Therefore, publishing / importing publications creates links between publications and CRIS entities (authors, departments and projects). In cases where they do not exist in CRIS, short corresponding CRIS entity records are created, which need to be supplemented with the necessary information. DSpace / CRIS ensures efficient collection, storage, search, navigation and dissemination of information.
Science publications
Authors or the Library upload (publish) research publications in the system (metadata along with full-text documents). In case the author uploads the research publications, they should be reviewed and approved by the Library (DSpace ensures this functionality). Publications in VDU research journals are uploaded by the Library. Full-text documents of research publications may be subject to embargo period or limited access, as appropriate, under the terms of the licensing agreement with the author or publisher.
Retrospective publications are imported from the library information system ALEPH (https://aleph.library.lt/F?func=find-b-0&local_base=vdu02) and legacy VDU DSpace repository. Part of the publications in ALEPH system do not have full-text documents. It is planned to review the possibilities to provide as many full-text publications as possible without infringing copyright.
ETD
Students (postgraduates, doctoral students) upload their final study papers (ETDs) themselves using DSpace functionality (placement forms, workflow, metadata and full-text documents). Library approves. Plagiarism check is done by supervisors using commercial or open-source plagiarism checking systems before uploading into Dspace.
E-journals
E-journals with publications are uploaded by the Library (metadata and full-text documents).
Researchers’ profiles, CV
The initial scientists profile data and CV are entered by the Library, and later the researchers update profiles themselves. The process is coordinated by the Library.
Projects
Projects are uploaded by Research and innovation department, coordinated by the Library.
ORCID
The ORCID is a nonproprietary alphanumeric code to uniquely identify scientific and other academic authors and contributors (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ORCID). Scientists can register in this system themselves (https://orcid.org) and enter their profiles, science publications and CV.
ORCID (Open Researcher and Contributor ID) – an international unique researcher identifier (personal reference, online profile) linking all research activity of a researcher and creating links with institutions that accumulate and use ORCID: publishers, databases, repositories, research organizations, professional associations, universities, science sponsors, e.g.: Clarivate Analytics, CrossRef, EBSCO, Elsevier, Emerald, F1000, Hindawi, Scopus, Springer Nature, WordPress, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, PLOS, etc.
ORCID – researcher is given a unique 16-letter (https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9335-3734) and numeric code, which identifies researcher. This code is important in determining the identity of the author and ensuring an appropriate affiliation for published research. This is to eliminate confusion when the names and surnames of the authors coincide, when the names change or in other cases.
DSpace / CRIS has a special connection module with ORCID.
For assessment - Scopus, Clarivate Web of Science, altmetrics, etc.
DSpace / CRIS has automatic interfaces with Clarivate Web of Science, Scopus and altmetric systems, can provide indicators from these systems.
Plagiarism control system
ETD are checked in external plagiarism control systems before uploading into repository:
- Open source plagiarism check systems, e.g.: Dupli Checker, Copyleaks, PaperRater, etc.
- Commercial plagiarism check systems, e.g.: iThenticate, Urkund, etc.
www.vdu.lt
Dissemination of research output and activities on the Internet should be done through the VDU main website, and all references to publications should begin www.vdu.lt. in case the systems and organizations that rank the university unambiguously identify the affiliation of these publications to VDU. www.vdu.lt in case the systems and organizations that rank the university unambiguously identify the affiliation of these publications to VDU.
OAI-PMH
The Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI-PMH) is a protocol developed for harvesting metadata descriptions of records in an archive so that services can be built using metadata from many archives (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protocol_for_Metadata_Harvesting). With this protocol, external systems can retrieve descriptive information (metadata) from repository and use for the repository contents dissemination on the internet.
Information System of Research Output Dissemination
Two main functions of this system:
- Generating reports and lists.
- Automatic data transfer to DSpace / CRIS and vice versa.
This system requires a database to transfer data from the repository and VDU IS. This system will have functionality that was in the legacy PDB (database of publications).
Report types:
- ŠMSM, LMT, MOSTA.
- Certifications.
- Contests.
- For authors.
- For departments.
- For administration.
Reports:
- Texts / lists.
- Analytic / statistic.
Altmetrics
Alternative indicators of research evaluation (Altmetrics):
- show how many research publications or data are read, debated, downloaded, recommended to others, cited;
- speed up usage data, no need to wait a year to see the impact of research results on science and its development;
- not only traditional publications are evaluated, but also influence on science of other sources of information, such as datasets, programs, blogs, videos, etc.;
- impact of research results on a wider audience - not just scientists, but also practitioners, doctors, educators and the general public is evaluated.
Altmetric tools (http://altmetrics.org/tools):
- Impactstory (https://impactstory.org).
- Plum Analytics (http://www.plumanalytics.com). .
- Altmetric (http://www.altmetric.com).
